1. Template Based Design Technique - Part 1
2. Template Based Design Technique - Part 2
Design Approach
During designing various systems for small and large companies, we have faced constant challenge of scalability, flexibility, performance. To tackle few of these challenges, we have developed our own pattern. It is named as Template Driven Design or the Template Pattern.
In a template pattern, the model (data such as XML,) has no inherent knowledge of how it would be utilized. The actual algorithm is delegated to the views, i.e. templates. Templates are applied to the different set of data and produce different results. Thus, it is a subset of model-view-controller patterns without the controller. For example, different XSLT templates could render the different XML data and produce different outputs.
Let us take an example to understand the challenge and then ways to resolve the same. We are very familiar with Microsoft Word. The users of MS Word can create template and further they can create document using templates. Suppose I wish to create my resume, I can use one of the several resume templates it provides to make one of mine. So now keeping template creation facility in view the whole process can be depicted as:
In this process “Resume Template” and “Resume“ have separate and distinct life cycles. Destruction of Resume does not affect “Resume Template”. Similarly destruction of “Resume Template “ does not affect “Resume “ once it is created.
This design pattern can be further explained below as:
1. If God is imaginative enough, he can accommodate all type of fields in his template even those will be required in future. We can consider God’s creation as Master Template which gives wisdom to angels to create Templates. In this terminology the “Master Template creator” acts as God. Assuming that the GOD knows only present in that case list of attributes are not final and it will not remain same for ever. Since GOD learns various new tricks over time period, so Master Template is not fixed and it also evolves over time period.
2. God can appoint various Angels (Template Creators), who can use one of the “Master templates” and can create templates for specialized purpose.
3. Now Human Beings (Resume Creators) can use one of the “Resume Templates” and can create various resumes.
So now question arises on how to implement same design pattern in a business application which could be web based. Assuming that the application is a web application and it is user creation service. Now keeping Template creation facility in view, the whole process of user creation service can be depicted as:
Let’s assume that God creates Master Template “MT1” with the following fields:
1. User Name
2. First Name
3. Middle Name
4. Last Name
5. Remarks
6. Gender
7. Status
Now the Angel (Template Creator) chooses the above Master template “MT1” and the following page will be displayed. (The significance of the other fields as mentioned below in the page, will be explained later in the document)
Now the Angel creates User Template “UT1” as shown below, with all the fields as specified in Master Template:
The user now chooses the above template “UT1” to create a new user and following page is displayed.
The user now fills this form with the following values:
User Name: Shilpi
First Name: Shilpi
Middle Name: Asnani
Last Name: Asnani
Remarks: Form created
Gender: Female
Status: Active
When the user clicks on save button, the data is stored in database. The data can be viewed back in following form:
Implementations Details
The following diagram covers the flow explained above. Also the Create/ Read/ Update/ Delete (CRUD) operations on form and Templates are covered in following sections.
GUI Interface component, as specified in diagram below, is used to generate master template XML documents. The XML file is compliant with the Master Template Schema.
After generation of XML file, a XSL designed for the Master Template is used to transform this XML document into HTML (Master Template).
Now on this HTML page (Master Template) the values are entered and data is saved in a XML file. The XML file is compliant with the Template Schema. The XSL designed for Templates is used to transform the XML document into HTML (Template).
The values are entered on the HTML (Template) page. On the click of the ‘save’ button by the user, the values are stored in the in a XML file/ database. The persistent XML is compliant with the ‘Generic Form’ schema.
To update the values, the data is retrieved from the database and a XML file is generated. Further an XSL designed for generic form is used to transform this XML document into HTML (Generic Form).On this HTML (Form) the values are edited and data is saved back into database.
Functional details:
Pre-requisite
• Copy all the schema files and XSL from the zip file in the directory “C:\Templates”
• Deploy the project “TemplateApproachProj” on JBoss
• Restore the SQL dump from the zip file in MySQL
The whole process flow is divided into 3 parts:
• Generate Master Template
• Generate Template
• Generate Forms
Generate Master Template
When the project (TemplateApproachProj) is launched then following screen is displayed:
Fig:2.1
The screen is used to generate Master Templates. The functionality of all the fields are explained below:
Master Template Name: This is the name of the Master Template
Master Template Description: This is the description of the Master Template
Field Name: The name of the field to be displayed on the form (e.g.: username)
Visibility: Two radio buttons indicating field’s display while creating a new form.
VisibilityInfoDisabled: If yes, then Angel can’t change the visibility status.
Mandatory: Two radio buttons specifying whether field is mandatory or optional while creating a new form.
MandatoryInfoDisabled: If yes, then Angel can’t change the mandatory status.
Input Type :Field on the form can be one of the 6 input types as listed below:
TextBox
TextArea
RadioButtonGroup
CheckBoxGroup
SingleSelectDropList
MultiSelectDropList
Specify Values for DropList: Specify the comma separated list of values for SingleSelectDropList, MultiSelectDropList, CheckBoxGroup, RadioButtonGroup input types.
JS File Required: If yes, then Angel can associate JS file.
Browse Button: Is used to select Master Template XML file.
Ok Button: Is used to create Master Template XML document with single element.
One More: Is used to create or add more elements in Master Template XML document.
Preview XML: Is used to view the elements of Master Template.
Let us create a Master Template. So specify the following details on the form (fig 2.1):
Master Template Name as “MT1”
Master Template Description as “Master Template added”
Field Name as “UserName”
Click “Yes” for JS File Required.
Click “One More“ button
Field Name as “Gender”
Input Type as “SingleSelectDopList”
Specify Values for DropList as “Male,Female,Not willing to reveal”
Click “One More” button.
Now the Master template file “MT1.xml “is generated at path “c:/Templates”.
Click on browse button to select Master Template XML file “MT1.xml “created above.
Click on “submit” button
The (Master Template) HTML page (fig 2.2) is displayed.
Note:
1. The convention is that the name of the Master Template XML file is name of the
Master Template.
2. All the templates will be stored at location “c:\Templates”.
Generate Template
After clicking the ‘Submit’ button as mentioned above, following screen will be displayed
Fig 2.2
This HTML form (Master Template) is used to generate Template. The functionality of all the fields are explained below:
Name: This is the name of the Template
Description: This is the description of the Template
Visibility: Checkbox indicating field’s display while creating a new form.
Mandatory: Two radio buttons specifying whether field is mandatory or optional while creating a new form
Validation File: Specify the path of the js file. The convention is that the name of the function in js file should follow the following format.
function func_fieldname(fieldId)
{
}
*The fieldname is the name of the field with which js file is associated.
*The input parameter fieldId is the id of the fieldname.
Event :Specify the event, on which the function in js file will be invoked, for that particular field of the form
Let us create a Template. So specify the following details on the form (Fig 2.2):
Template Name as “UT1”
Template Description as “Template added”
Validation File as “test.js”
Event as “onchange”
Click “Save” button.
Now the template file “UT1.xml “ is generated at path “c:/Templates”.
The below mentioned screenshot fig 2.3 is displayed
Click on browse button to select Template XML file “UT1.xml “created above.
Click on submit button
The (Template ) HTML page (fig 2.4) is displayed
Note: The convention is that the name of the Template XML file is name of the Template.
Fig 2.3
Generate Object
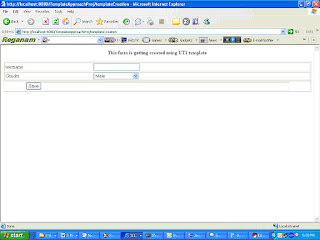
After clicking the submit button as mentioned above following screen will be displayed
Fig 2.4
The values are entered on the HTML(Template) page. On the click of the ‘save’ button, a user is created.
The field username/Gender displayed on the above screen was specified in Master Template/Template.
Let us create a user. So specify the following details on the form:
User Name as “Shilpi”
Gender as “Female”
Click “Save” button.
Data is saved in database.
The below mentioned screenshot (fig 2.5) is displayed
Click on id (let say object id 47) created above.
The data is retrieved from database and displayed on HTML page(fig 2.6)
Change username as “ShilpiAsnani”
Click on save button
The data is updated in database and the below mentioned screenshot (Fig 2.7) is displayed
Fig 2.5

Fig 2.6

Fig 2.7














No comments:
Post a Comment