Service can be defined as system or organization that provides stakeholders with some thing that they need/ask for or and consequence of execution of it.
Stakeholders involved may be people, organizations or systems.
Stakeholders:
1. Client
a. Citizen
b. Business
c. Public Administration Organization
2. Service Organization
a. Service Provider
b. Evidence Verifier
c. Evidence Provider
i. Primary
ii. Auxiliary
d. Consequence (Auxiliary Outputs) Receiver
e. Primary Output Receiver
3. Service Broker
a. Service Repository
b. Interoperability Agent
Service Interaction:
The Client contacts a Service Provider (Public Administration Organization) and asks for a service that requires for its execution input from organizations located in national/states/municipalities across India. The Service Provider, after gathering from these countries all evidences needed for Service execution, executes the Service based on predefined Rules and provides Client with an output (Primary Output) and all organizations with the consequences (Auxiliary Outputs) of the Service.
Preconditions:
A client identifies service organization and ensures that potential service exists. Client provides minimum set of evidences (primary inputs) needed for initiating the service identification. Client may also supply Auxiliary inputs ( in form of evidences and references to evidences) as required by service contract.
Post conditions:
Client receives the Output (primary output) of service execution and participatory organizations receive consequences (Auxiliary Outputs).
Interaction Model:

Description:
Participating Roles
Client
Primary Output Receiver
Service Provider
Broker (Service Repository, Interoperability Agent)
Evidence Provider
Evidence Verifier
Consequence Receiver
Description of Steps
Step 1. A client requests for service. He/she supplies some evidences and some references to evidences. Evidence supplied by client may be categorized as:
1. Evidence required for identification purpose
2. Evidences needed to fetch more evidences from evidence providers
3. Evidences needed to execute service
Less evidences supplied by client to Service Provider, transparent is the service. Of course number and type of evidences required are service specific.
Step 2. Service provider supplies the evidences/credentials of client Broker that in turn passes the same to Evidence Verifier. Evidence Verifier verifies credentials of Client and accordingly supplies the results to Service provider via Broker. Now Client has an Identity.
Step 3. Service Provider looks up for more evidences on the based of identity established for client and references provided by client with the help of Evidence Providers via Broker.
Step 4. Evidences collected from Client, Evidence Suppliers are passed to Evidence Verifiers via Broker.
Step 5. On positive out come of Evidence Verifiers, Service is executed. The outcomes of service are passed to Primary and Auxiliary Output Receivers.
Class Model:
The interaction model can be depicted in class model in two parts
1. The Operational (Transactional) Part
2. The Knowledge (Planning) Part
The Operational Part
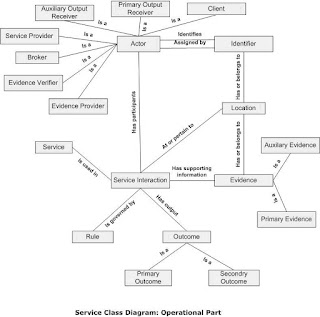
The Knowledge Part

Reference:
1. Fowler, M., Analysis Patterns. Object Technology Series, 1997: Addison-Wesley




No comments:
Post a Comment